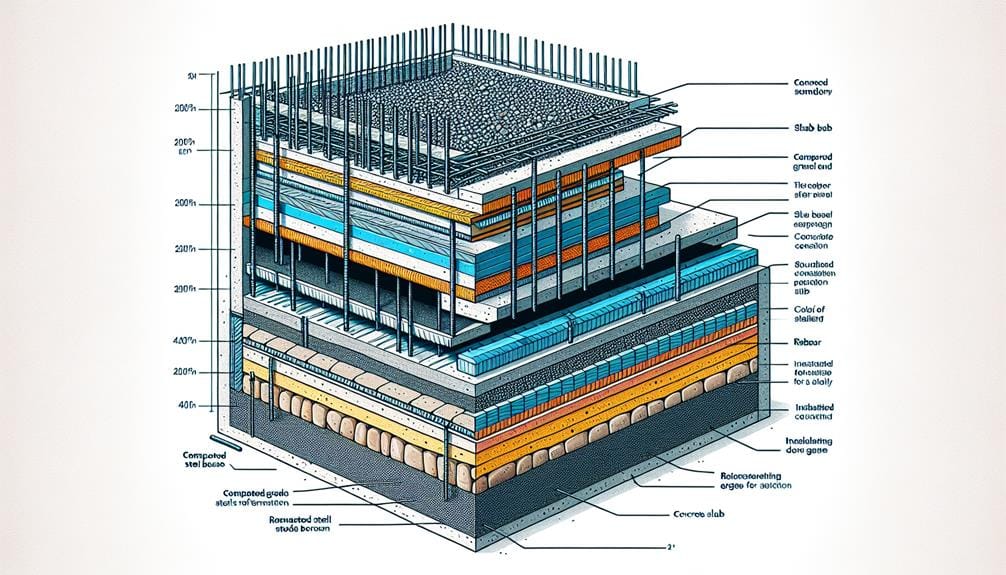
3 Essential Tips for Slab on Grade Foundations
Foundation preparation, slab thickness considerations, and selecting the right materials are key.
Key Takeaways
- Ensure the ground is level, compacted, and free of debris or obstructions before laying the slab.
- Determine slab thickness based on the structure type and load-bearing capacity.
- Implement sufficient drainage measures such as French drains or sump pumps to enhance foundation longevity.
- Select a concrete mix that provides sufficient strength and climate resistance for the slab.
Foundation Preparation
To guarantee a sturdy and even slab-on-grade foundation, we must meticulously prepare the ground by leveling it, compacting the soil, and removing any debris or obstructions that could affect the slab's structure. Adequate foundation preparation involves employing efficient soil compaction techniques to ascertain the site's stability. This can include using compacting tools like plate compactors or hand tampers to achieve the exact level of compaction required for the soil type. It's also essential to address potential drainage issues, which can drastically impact the longevity of the foundation. Implementing effective drainage solutions such as installing French drains, sump pumps, or having a compacted rubble trench around the perimeter can greatly reduce moisture-related problems. By devoting the necessary time and resources to foundation preparation, we can create a robust slab-on-grade foundation that is capable of withstanding the elements and providing a secure base for the structure it supports.
Slab Thickness Considerations
After ensuring a stable and level ground by thoroughly compacting the soil and addressing drainage concerns, we need to contemplate another critical factor: the precise thickness of the slab. This measurement plays a significant role in maintaining the structural integrity and energy efficiency of our building.
When determining the slab thickness, we must consider various factors, including the type of structure, load bearing capacity, and insulation requirements. In general, a typical slab thickness ranges from 4 to 6 inches. However, if the building is expected to bear heavy loads or if additional insulation is necessary, this thickness might need to be adjusted. The table below outlines some general guidelines for slab thickness.
| Structure Type | Load Bearing Capacity | Insulation Requirements | Suggested Slab Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | Light | Basic | 4-5 inches |
| Commercial | Medium | Moderate | 5-6 inches |
| Industrial | Heavy | High | 6-8 inches |
Common Material Choices
Guaranteeing a robust concrete slab requires careful selection from a range of materials that will effectively complement the structure's needs. As builders, we recognize that the right materials can make all the difference in the durability and performance of a slab-on-grade foundation.
In terms of concrete types, it is essential to choose a mix that offers adequate strength and resistance to the local climate conditions. For areas with high temperature variations, a concrete with increased thermal mass can help maintain a consistent indoor temperature. For buildings in flood-prone regions, using water-resistant concrete can minimize damage in the event of flooding.
Another pivotal aspect to take into account is insulation options. Proper insulation guarantees that the slab remains warm during colder months and cool during the warmer months, reducing heating and cooling costs. Common insulation materials for slab-on-grade foundations include foam board, fiberboard, and reflective insulation. By carefully selecting the appropriate concrete type and insulation, we can ascertain that our slab-on-grade foundation is robust, efficient, and environmentally friendly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Primary Differences Between Slab-On-Grade and Crawl Space Foundations?
"We differentiate between slab-on-grade and crawl space foundations by their construction and advantages. Slabs offer cost-effectiveness, durability, and fewer maintenance issues, while crawl spaces provide easier access for repairs and future remodeling."
Can Slab-On-Grade Foundations Be Used for Projects Other Than Residential Buildings?
"Yes, we use slab-on-grade foundations for way more than houses: commercial applications abound, like retail centers and office buildings, and even industrial structures benefit from their efficiency and durability."
How Can the Risk of Soil Settlement Be Mitigated During Foundation Construction?
When constructing slab-on-grade foundations, we guard against soil settlement by using soil compaction techniques to guarantee stable grounds and implementing moisture management strategies to regulate soil moisture and prevent expansive soil movement.
What Impact Does the Porosity of Concrete Have on the Foundation's Performance?
'We find that the porosity of concrete greatly affects the foundation's performance. As concrete permeability allows moisture retention, it can exacerbate settlement issues, making preventative measures like proper soil preparation and moisture control essential.'
Are Slab-On-Grade Foundations Less Susceptible to Pest Damage?
Use moisture barriers to prevent pest infestations in slab-on-grade foundations. Without these barriers, pests like termites can cause significant damage. As we recognize the benefits of slab-on-grade foundations, we must also address these vulnerabilities.